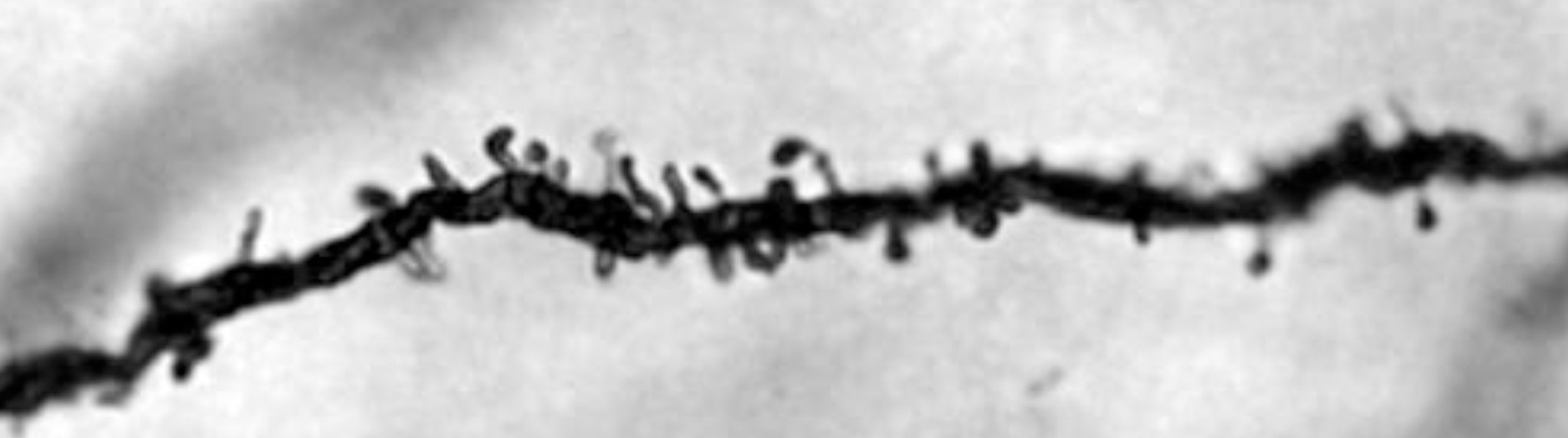
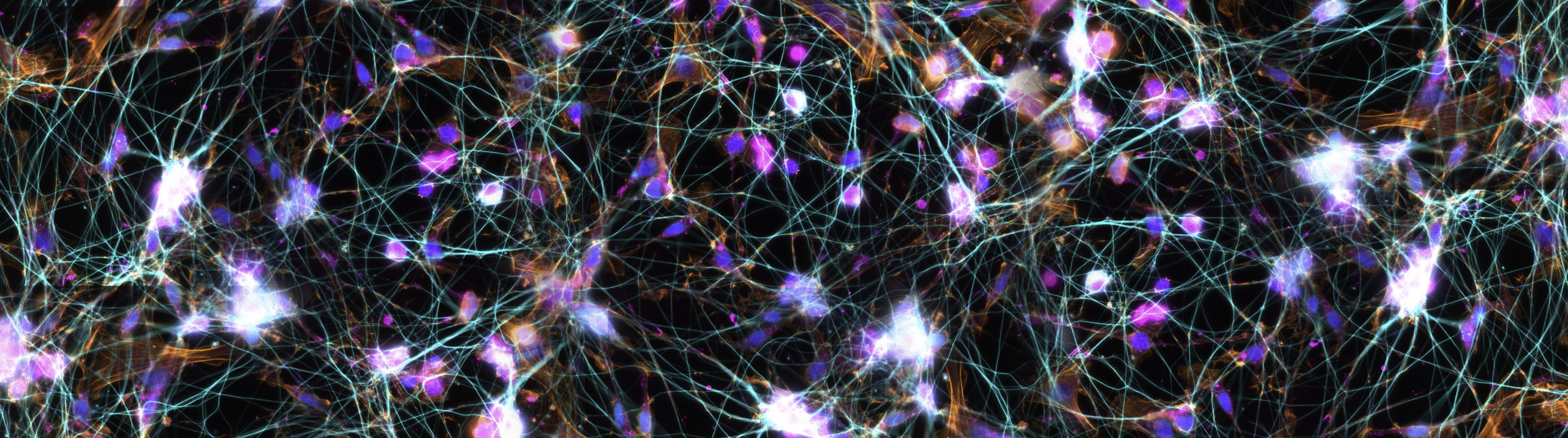
In spring, days grow long, and the white-footed mouse looks for a mate. For some mammals, day length prompts behaviors like breeding or camouflaging, and scientists say it's not just the arc of the sun that kicks off these seasonal events; substances in the brain also play a part. One important element is melatonin, a hormone that the mammalian brain secretes at night. According to a...
Read MoreSoftware & Microscope Integrated Systems
Drugs affect different people in different ways. Take cocaine for example. Not only does the drug have a stronger impact on the behavior of individuals with a particular genetic makeup, it also initiates more profound changes in their brains. Researchers at the University of Michigan are studying brain plasticity in cocaine-treated rats after a period of abstinence. They're studying how abstinence from the drug affects different...
Read MoreSensory stimuli are all around us. Street traffic zooms by. A neighbor waves “hello.” A co-worker taps away at his keyboard. Each sight, sound, and motion ignite action within our brains. But even without all these stimuli, the brain is always active. Known as “spontaneous activity,” the activity happening inside the brain in the absence of direct stimuli follows a pattern of up and down states...
Read MoreLife's little pleasures often elude those suffering from depression, including rats, who show little interest in sugar water after experiencing stress. This behavior leads scientists to speculate that the illness might be characterized by a defect in the brain's neural reward circuit. Recent research focuses on a key element of this circuit – the nucleus accumbens (NAc), part of the brain region known as the ventral...
Read MoreScientists hypothesize that seizures occur because brain cells fire in places they're not supposed to. Dentate granule cells (DGCs), a type of neuron born throughout adulthood, sometimes migrate into a different region of the dentate gyrus, a part of the hippocampus. These abnormal newborn cells sprout axons called “mossy fibers” that form connections with neighboring DGCs in the inner molecular layer, causing synaptic changes that...
Read MoreThe placenta delivers nutrients from a mother's blood to a developing fetus. It also produces hormones that help the baby grow during its forty or so weeks in utero. But the placenta's powerhouse abilities don't end there. The organ provides a wealth of information about the infant's future health, allowing doctors to make predictions about whether or not the child will develop autism or, later...
Read MoreIf one area isn't working, another part can step in. Plasticity is one of the brain's most beautiful attributes. Recent research has documented the organ's ability to compensate in the face of damage, and now a new study identifies a key region for compensation when the damage occurs in the hippocampus. The region is the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). It's an integral part of the hippocampal-prefrontal-amygdala...
Read MoreObstetricians and midwifes have long hailed the benefits of folic acid during pregnancy. Now new research offers evidence that choline is another important nutrient for the developing fetus. Found in foods like eggs and cauliflower, choline is known to aid healthy liver function. But in the past few years, studies have shown that the nutrient also plays a role in brain development. One recent study...
Read MoreAccording to scientists at the Hotchkiss Brain Institute in Calgary, Canada, there is evidence for increased neurogenesis in adult mice reared by two parents. Their study also describes other interesting findings, such as the fact that increased neurogenesis persists in the next generation, or that the effects of differences in rearing affect males and females differently. Using Stereo Investigator to perform a stereological assessment of proliferating cells...
Read MoreResearchers at the Waisman Center (University of Wisconsin-Madison) just took a big step in their quest to develop regenerative medicines for treating Parkinson's, Alzheimer’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. They used human embryonic stem cells to restore memory and learning in disabled mice. The study, published last month in Nature Biotechnology, "is the first to show that human stem cells can successfully implant themselves in the brain...
Read More